Characteristics of Oil and Gas
Characteristics of Petroleum
Nearly all naturally occurring petroleum deposits are made up of an extremely large number of petroleum compounds, all mixed together. Molecules of all these compounds are composed of the chemical elements hydrogen and carbon in various proportions. Petroleum compounds of these elements are called hydrocarbons, and each compound is made up of a different proportion of the two elements. Seldom are two crude oils found that are seemingly identical and certainly never are two crude oils made up of the same proportions of the various compounds. Within a single petroleum deposit, the mixture differs some from place to place and in many cases to an extreme degree.
Components of Petroleum
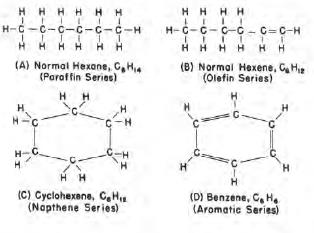
The vast number of hydrocarbon compounds making up petroleum have been grouped chemically into series of compounds. Each series consists of those compounds similar in their molecular make-up and characteristics. Within a given series, there exist compounds from extremely light, or chemically simple, to heavy, or chemically complex. As an analogy, the hydrocarbons may be compared to cattle; just as cattle are classified into different breeds, hydrocarbons are classified into different series. Just as there are a multitude of different cattle sizes within a breed, within a hydrocarbon series, there are a multitude of compounds that differ due to the weight of the molecules of which they are made.
The most common and greatest number of hydrocarbon compounds making up a naturally occurring petroleum deposit are those of the paraffin series, which includes methane, ethane, propane, butane and others. Because of this, it has been the practice in the petroleum producing industry to analyze all petroleum samples according to their fractional composition based on the boiling properties of the various paraffin series constituents.
The composition of most petroleum deposits will include some quantity of nearly all components throughout the entire range of weights and complexities, whether the hydrocarbon is heavy crude oil with characteristics approaching tar, or the lightest of natural gases from which liquids can be condensed only with great difficulty. Gas, therefore, is not a gas because it is composed entirely of light molecules which are different from those making up crude oil. Naturally occurring gas is different because the majority of its component molecules are lighter and simpler, whereas liquid crude oil is made up of a majority of the heavier and more complex component molecules. Both natural gas and crude oil, however, contain some of most all existing hydrocarbon components.
Structural formulas of four hydrocarbon series (compounds containing six carbon atoms). Structural formulas of the four lightest paraffin compounds
keywords: hydrocarbon, paraffin, Components, Petroleum.



Comments